Archive
Semantic Network according to John F. Sowa
 John Florian Sowa is the computer scientist who invented conceptual graphs, a graphic notation for logic and natural language, based on the structures in semantic networks and on the existential graphs of Charles S. Peirce.
John Florian Sowa is the computer scientist who invented conceptual graphs, a graphic notation for logic and natural language, based on the structures in semantic networks and on the existential graphs of Charles S. Peirce.
John F. Sowa said:
“A semantic network or net is a graphic notation for representing knowledge in patterns of interconnected nodes and arcs.” Read more…
Getting close to Google Scholar

When we are thinking on writing an academic document, we are asked -and must- to use reliable information sources, that is where Google Scholar can help us. This information management tool search internet in order to find acamedic works related with the topics you ask to. One of the features which make Google Scholar such a good searcher is that it gives a short description, and also the times it has been cited. That is why when I was writing my class record about Google Scholar, I use it to get information about itself, and this is what I found: Read more…
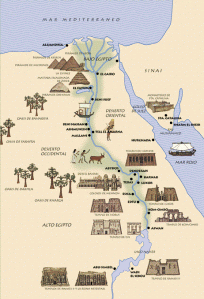
Ancient Egypt World
The more than 3000 year long history of Ancient Egypt has been divided into 8 or 9 periods, sometimes called Kingdoms. This division is based on the country’s unity and wealth and the power of the central government. The Ancient Egyptians seem to have developed the notion of dynasties throughout their history.
The ancient Egyptians thought of Egypt as being divided into two types of land, the ‘black land’ and the ‘red land’.
The ‘black land’ was the fertile land on the banks of the Nile. The ancient Egyptians used this land for growing their crops. The ‘red land’ was the barren desert that protected Egypt on two sides. This desert protected ancient Egypt from neighbouring countries and invading armies. It also provided the ancient Egyptians with a source for precious metals and stones.
The Egyptian life
Daily life in ancient Egypt revolved around the Nile and the fertile land along its banks. The people of ancient Egypt built mudbrick homes in villages and i the country. They grew some of their own food and traded in the villages for the food and goods they could not produce. Most ancient Egyptians worked as field hands, farmers, craftsmen and scribes. A small group of people were nobles.
The Pharaoh
The most powerful person in ancient Egypt was the pharaoh. The pharaoh was the political and religious leader of the Egyptian people, holding the following titles: ‘Lord of the Two Lands’ and ‘High Priest of Every Temple’.
As ‘Lord of the Two Lands’ the pharaoh was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned all of the land, made laws, collected taxes, and defended Egypt against foreigners. As ‘High Priest of Every Temple’, the pharaoh represented the gods on Earth. He performed rituals and built temples to honour the gods.
Many pharaohs went to war when their land was threatened or when they wanted to control foreign lands. If the pharaoh won the battle, the conquered people had to recognise the Egyptian pharaoh as their ruler and offer him the finest and most valuable goods from their land.
The Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt
The ancient Egyptians believed in many different gods and goddesses. Each one of these gods and goddesses played it own role to maintain peace and harmony across the land.
Some gods and goddesses took part in creation, some brought the flood every year, some offered protection, and some took care of people after they died. Others were either local gods who represented towns, or minor gods who represented plants or animals.
The ancient Egyptians believed that it was important to recognise and worship these gods and goddesses so that life continued smoothly.
The Pyramids and Temples
As everybody knows, egyptians used to built pyramids as tombs for their pharaohs and their queens.
The pharaohs were buried in pyramids since before the beginning of the Old Kingdom to the end of the Middle Kingdom. There are about eighty pyramids known today from ancient Egypt. The three largest are located at Giza. The most well-known of these pyramids was built for the pharaoh Khufu. It is known as the ‘Great Pyramid’.
Egyptian temples were built for the official worship of the gods and commemoration of the pharaohs. Temples were seen as houses for the gods to whom they were dedicated. In them, the Egyptians performed a variety of rituals: giving offerings to the gods, reenacting their mythological interactions through festivals, and warding off the forces of chaos. These rituals were necessary for the gods to continue to uphold maat, the divine order of the universe. pharaohs delegated their ritual duties to a host of priests, and most of the populace was excluded from direct participation in ceremonies and forbidden to enter a temple’s most sacred areas. In conclussion, a temple was an important religious site for all classes of Egyptians, who went there to pray, give offerings, and seek oracular guidance from the god dwelling within. 
Egyptian Writting
To end with this tour for the most important points of the Egyptian world, I would like to speak about their writting. It is one of the most ancient and complex of the world.
The invention of the writing towards 3000 B.C. determines the beginning of the Egyptian history more than any other change. The possibility of reading and writing make the difference between the principal cultures of the Near East and the contemporary cultures, opening new possibilities. The writing was complex and the aptitude to read and write was remaining limited to a minority, up to the diffusion of the alphabetical writing, the society could not exploit the whole potential that the writing supposed.
Along the Egyptian history, three types of writing were developed:
The hieroglyphic or hieroglyphic monumental, used in inscriptions of monuments and decorations. It is the most ancient and more complex type of writing and was used since 3100 B.C. It was a type of sacred, so called writing ” writing of the god’s word “, and as a sacred writting, it was using in sarchofagi, tombs, monuments and sculptures, and was represented with great details. it could be written in any sense (except bottom up) and in lines or columns.
The Hieratic: It arose as brief writing of the hieroglyphic cursive one and it was the writing used by scribes (that were not forced to know the hieroglyphic one) and for the priests in literary copies.
The hieroglyphic cursive one disappeared concerning 1000 B.C. whereas the hieratic was in use in religious texts up to ends of the Egyptian civilization. Also it was using in scientific texts and literary works. It was a type of very useful writing in papyruses and ostracas. It was written in black ink with a sharp cane and the red ink was using as rebearing of certain paragraphs.
Mey Ling Núñez. 19/03/2012
References
- Ancient Egypt, British Museum. http://www.ancientegypt.co.uk/menu.html
- The Ancient Egypt Site by Egyptologist Jacques Kinnaer. http://www.ancient-egypt.org/
- Discovering Ancient Egypt by Mark Millmore. http://www.eyelid.co.uk/
- BBC History. Ancient history. Egyptians. http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/ancient/egyptians/
Protecting Ownership

”A lot of information is available to you on the Internet. But the fact that you can access that information does not mean it is proper or safe to use it any way you want” (Freedman, Jeri: “Intellectual Property“).
The writer Jeri Freedman has dealt with the issue of intellectual property in her book “Cyber Citizenship and Cyber Safety. Intellectual Proeprty”. She emphasizes in the responsible use of Internet, pointing out that there are sometimes strong feelings of property while concerning creative works those feelings are not taken into account. A similar opinion is given by Jennifer Peloso, who deals with related prolems like plagiarism, piracy and copyright; or Mary Pilon, who talks about the misuse students give to the Net and takes the intellectual property issue into the education field. Nevertheless, if Lauwrence Lessing’s video on “Freeing Culture” is taken into account, we will see that there is a discussion concerning intellectual property and that there are different points of view regarding this problem. How should we solve it without forgetting all the actors? Read more…